Digital maps play a key role in modern urban planning, disaster preparedness, and environmental monitoring, providing the tools needed to create safer and more sustainable territories. These maps provide precise geospatial data, empowering governments, businesses, and organizations to make informed decisions in flood-prone areas.
Recently, many regions around the world have been affected by devastating floods. The most vulnerable to flooding are areas with low-lying terrain, developed river systems, and heavy rainfall. For example, this applies to parts of South Asia (India and Bangladesh), Southeast Asia, as well as floodplains in North America and Europe. Rising sea levels and extreme weather events associated with climate change are further increasing flood risks worldwide.
Types of Digital Maps Crucial for Resilience
- 3D Maps
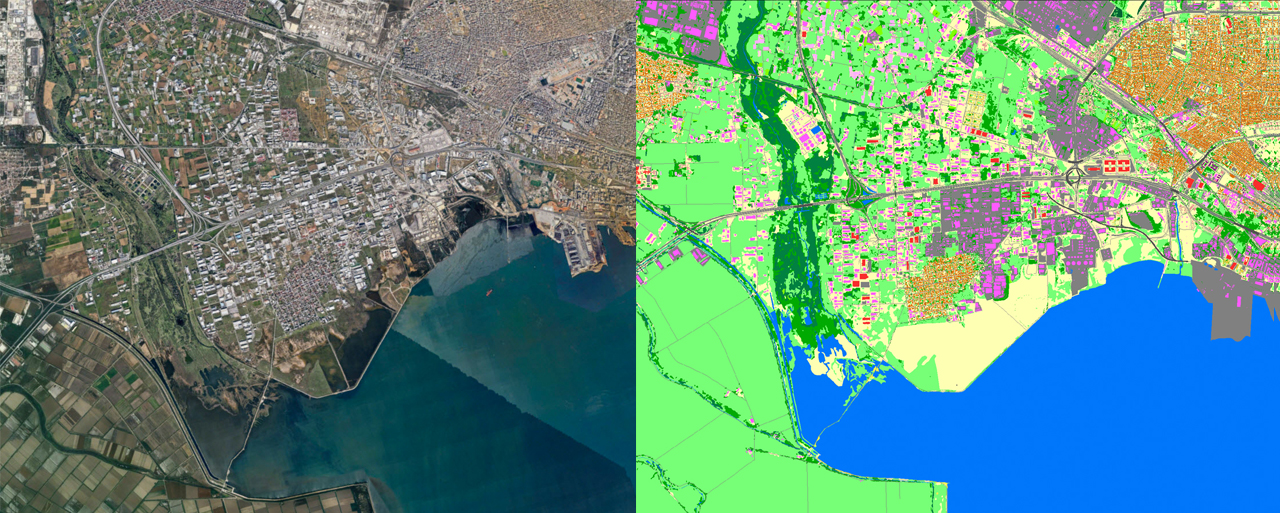
High-resolution 3D maps provide a detailed view of the urban environment, including building heights, vegetation, and other structures. These maps are essential for planning infrastructure, evaluating flood risks, and telecommunications network development. For instance, mapping vegetation patterns in urban areas helps analyze water runoff patterns and improve drainage systems. - Population Density Maps
These maps show the distribution of the population during the day and night, aiding emergency response and resource allocation. During a disaster, such as the Kakhovka Dam flooding, population density maps ensured effective evacuation planning for the most affected areas. - Land Use and Clutter Maps
These maps categorize areas into residential, commercial, industrial, or natural zones. Land use analysis helps identify vulnerable areas, optimize urban development, and reduce environmental impact. - Digital Terrain Models (DTMs)
DTMs represent surface elevation without accounting for objects like trees or buildings, making them invaluable for flood modeling, drainage design, and infrastructure planning. - Digital Surface Models (DSMs)
DSMs include all surface features, such as vegetation and buildings, aiding in obstacle analysis for telecommunications and visualizing flood-prone areas. - Hydrological Maps
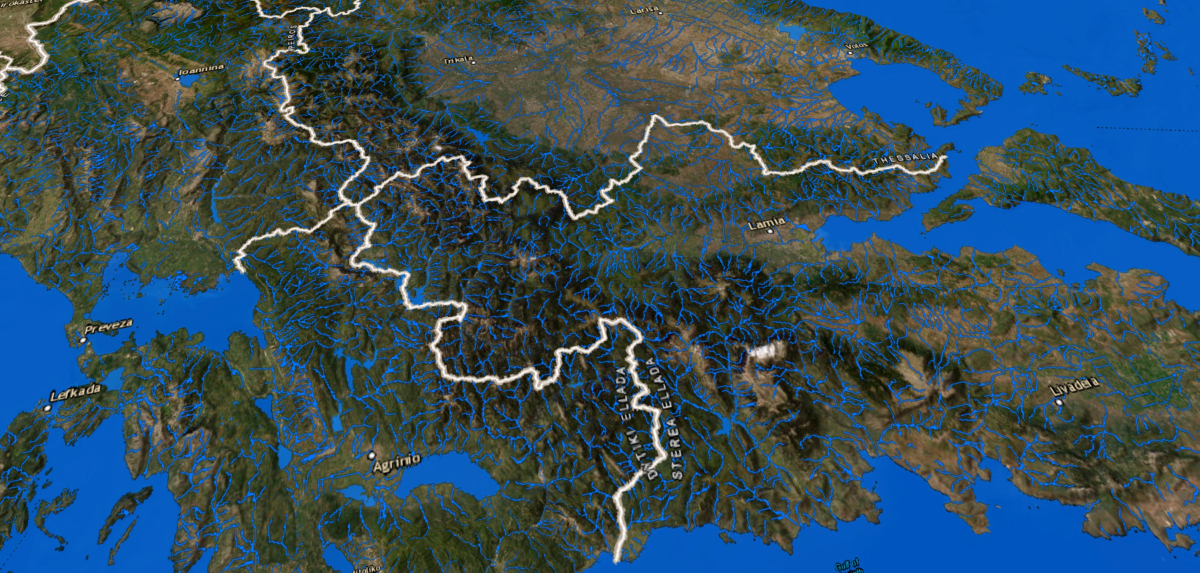
Focused on water systems, these maps help monitor river flows, flood basins, and changes in water levels, supporting early flood warning systems.
Sustainable Future Through Mapping Technologies
Nearly half of the European Union's population lives within 50 kilometers of the coastline. In the face of climate change and frequent flooding across Europe, developing effective flood management strategies is crucial to mitigating future risks. For instance, accurate and up-to-date geospatial land use data (Clutter/Land Use models) can assess the effectiveness of drainage systems, identify flooding risks in residential areas, evaluate the need for additional protective measures, and calculate the optimal locations for new green zones to enhance water absorption.
Investments in various types of digital maps provide a comprehensive understanding of the environment. They contribute to urban planning, enhance disaster response, and support environmental sustainability. By integrating these maps with strategic approaches focused on local communities, countries can effectively address climate challenges and foster safer, more adaptive societies. The incorporation of these tools across various sectors paves the way toward a more secure and sustainable world.