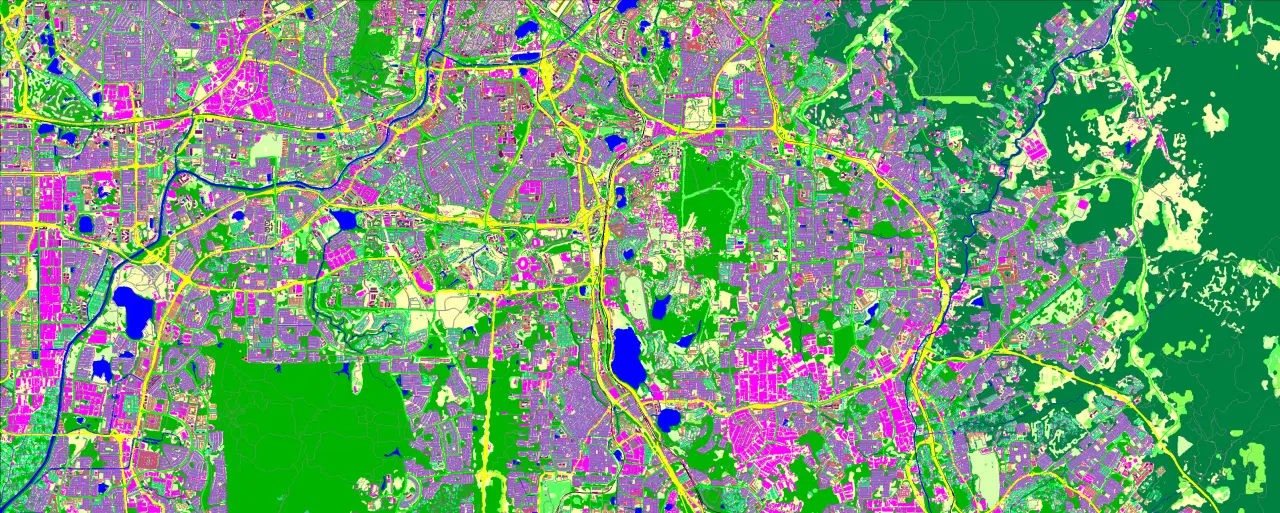
The key role of land use classification in wireless network planning, urban planning, resource management, and environmental monitoring
Clutter Modeling, an essential component of geospatial analysis, has evolved significantly with the integration of advanced algorithms and spatial analysis tools.
At the forefront of this evolution are Machine Learning Techniques, which leverage complex algorithms to extract meaningful patterns from cluttered datasets. By training models on large volumes of labeled data, machine learning algorithms can autonomously identify and classify different types of clutter, leading to more accurate clutter models.
Remote sensing technologies are crucial in clutter modeling by providing high-resolution imagery and other geospatial data sources. These technologies, including satellite imagery, aerial photography, and LiDAR data, offer rich sources of information for characterizing land cover, terrain features, and built-up areas. By incorporating remote sensing data into clutter modeling workflows, analysts can improve the spatial accuracy and detail of clutter models, enabling better decision-making in various applications.
Geospatial data analytics serves as the backbone of advanced Clutter Modeling. Through techniques such as spatial interpolation, spatial clustering, and spatial regression, analysts can identify spatial patterns, relationships, and trends within cluttered environments. These insights are instrumental in calibrating clutter models and validating their accuracy against ground truth data.
This analysis is fundamental in dynamic environments such as urban areas, where land use and land cover change rapidly.
Furthermore, advanced clutter modeling techniques enable analysts to integrate multi-source and multi-resolution data, providing a holistic view of cluttered environments.
Clutter analysis, in conjunction with urban land use modeling, enables planners to assess the connectivity and accessibility of urban areas, identifying transportation corridors, pedestrian pathways, and public spaces that are integral to the vibrancy and functionality of modern cities. By analyzing clutter patterns along transportation networks, planners can identify opportunities to enhance mobility, improve pedestrian access, and create vibrant urban hubs that promote social interaction and economic activity.
In conclusion, the adoption of advanced techniques such as machine learning, remote sensing technologies, and geospatial data analytics has revolutionized Clutter Modeling, offering new insights and capabilities for characterizing cluttered environments.
By leveraging these techniques, analysts can develop more accurate, reliable, and actionable clutter models that support a wide range of applications, from urban planning and infrastructure development to environmental monitoring and disaster management.
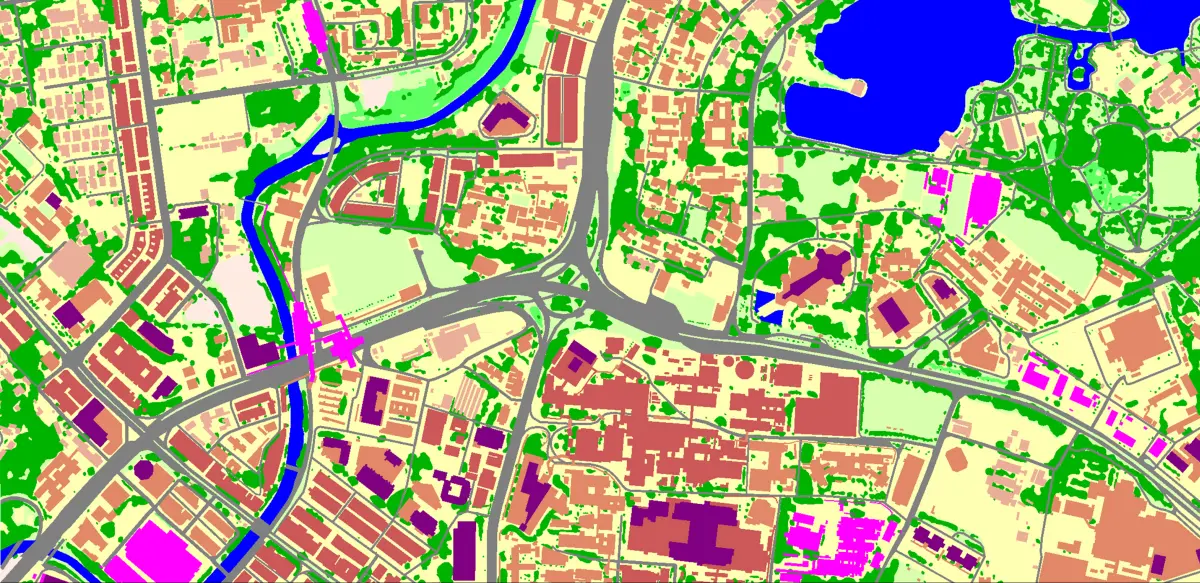
Visicom clutter models
Land Cover surface features are classified into different classes: classes of built-up areas, water classes, and classes of landscape and vegetation.
This level of classification depends on particular applications: urban, suburban or regional. For example, the ‘urban and built-up’ class includes ‘residential,’ ‘commercial,’ and ‘industrial’ subclasses. Correspondingly, each class can be subdivided into more detailed classes - subclasses.
Land Use details vary from 12 to 32 Clutter classes, from general map morphology to separate buildings in terms of meeting the concrete project needs.
Clutter Model is the essential part of each model we produce: 3D, 2.5D and 2D. As a rule, Clutter is generally produced from multispectral satellite imagery by automatic and partly manual photo-interpretation. We use AI-based System for detecting and extracting features from source imagery.
The accuracy and detail of the Clutter Model are particularly important for planning 5G in cities.
There are many types of clutter which prevent the propagation of mmWave 5G signals such as buildings and trees. That’s why the clutter classes for 3D city models include classification by height and vegetation types and heights as well.
Clutter data are also a key input for the production of Population Distribution models for RF planning tools like Atoll.
Together, they provide the information needed for network planning, optimization, and geomarketing, making them indispensable for telecom companies.
Depending on the project in could be supplied in 1m, 2m, 5, 10m, 20m, 50m resolution matrixes.
We utilize the most up-to-date satellite images and machine learning techniques to produce highly accurate Clutter Matrixes with 2-4m accuracy in-plane. Along with multiple geodata layers such as 3D Buildings, 3D Trees, Digital terrain models (DTM), Vector of streets and roads, Water objects, and Population data you obtain the full information required to calculate and simulate the signal propagation predictions.
Feel free to contact us for free samples and more information about Clutter models and PopMaps for 2D/2.5D/3D geodata.